https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.15831
NV-Retriever: Improving text embedding models with effective hard-negative mining
Text embedding models have been popular for information retrieval applications such as semantic search and Question-Answering systems based on Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). Those models are typically Transformer models that are fine-tuned with cont
arxiv.org
| 🔍 문제 상황 | - Contrastive learning 기반 text embedding 모델은 RAG·QA 등에서 중요한 역할을 함 - 모델 성능 향상을 위해 Hard-negative mining이 핵심인데, 기존 연구는 방법론이 불투명하거나 정량적 비교 부족 - 특히 false negative 문제로 인해 모델이 잘못 학습되며 성능이 저하될 수 있음 |
| 🎯 연구 목적 | - Positive-aware hard-negative mining 방법을 설계하여 false negative를 줄이고 효과적인 contrastive 학습을 가능하게 함 - 다양한 teacher model, mining 방법 비교 실험을 통해 best practice 제시 - 실제 대규모 모델 학습(NV-Retriever-v1)에 적용하여 SOTA 성능 달성 |
| 🧠 방법론 | 1. Positive-aware Hard-negative Mining • TopK-MarginPos: negative_score < positive_score - margin • TopK-PercPos: negative_score < positive_score × percentage (최고 성능) 2. Teacher 모델 다양화 • BM25, e5, Mistral 기반 모델 등으로 hard negative 후보 추출 3. Ensembling • 여러 teacher 모델 결과를 합침 • Intra-sample 방식(중복 허용)이 성능 우수 4. Sampling • TopK 후보 중 무작위 선택 (Top-1+sampled 방식이 일부 효과적) |
| 🧪 학습 데이터 | 총 70만+ 쿼리 • MS MARCO • Natural Questions (NQ) • SQuAD • StackExchange • HotpotQA, FiQA2018, etc. |
| ⚙️ 학습 방법 | - Base model: E5-large-unsupervised (334M), Mistral-7B-v0.1 (7.1B) - Contrastive loss (InfoNCE) 기반 학습 - Hard-negatives: Teacher model로 mining → Positive-aware 필터 적용 - 2단계 학습 (NV-Retriever-v1): 1단계: Retrieval task 중심 + in-batch negative 2단계: Classification, STS 등 다른 task 혼합 fine-tuning |
| 📊 실험 결과 | 🔸 RQ1 (Teacher 영향) • e5-mistral-7b-instruct > NV-Embed-v1 > snowflake > e5-v2 > BM25/random 🔸 RQ2 (Ensembling) • Intra-sample(no-dedup) 방식이 단일 teacher보다 더 우수 🔸 RQ3 (Mining 기법) • TopK-PercPos (95%)가 가장 높은 NDCG@10 성능 • Mistral 기반 대규모 실험에서도 동일한 경향 • false negative 비율 약 50% 감소 • Loss 분포 안정화, 학습 수렴 향상 |
| 🏆 NV-Retriever-v1 | - Base: Mistral-7B + bi-directional attention - TopK-PercPos(95%)로 mining - 평균 NDCG@10 = 60.9 → MTEB Retrieval 리더보드 1위 |
| 🌟 기여 | - False negative 제거에 최적화된 positive-aware mining 방법 제안 - 다양한 teacher/model 기반 ablation으로 하드네거티브 mining의 민감도 실증 - 실제 SOTA 모델(NV-Retriever-v1) 학습에 적용하여 성능 입증 |
| ⚠️ 한계 | - Mistral 기반 대규모 실험은 자원 소모 큼 (8×A100 기준 학습 90시간) - Classification 등 다른 task에 mining 기법 일반화는 추후 과제로 남음 - Instruction 기반 fine-tuning이 포함되어 있어 실험 재현 복잡도 ↑ |
https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.14233
Large Language Models are Strong Zero-Shot Retriever
In this work, we propose a simple method that applies a large language model (LLM) to large-scale retrieval in zero-shot scenarios. Our method, the Language language model as Retriever (LameR), is built upon no other neural models but an LLM, while breakin
arxiv.org
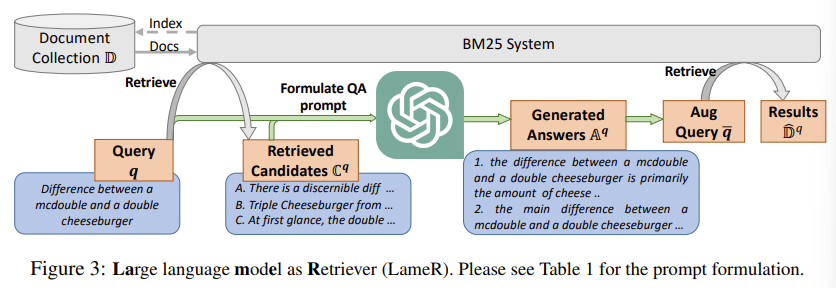
| 🧩 문제 상황 | - 기존 zero-shot retriever (특히 self-supervised dense retriever)은 성능이 낮음 - LLM 기반 쿼리 증강(HyDE)은 intent/context를 몰라 spurious out-of-domain 답변 생성 - LLM 출력은 dense retriever와 부조화되어 검색 품질 하락 |
| 💡 제안 방법 (LameR) | LLM + BM25 기반 2단계 Retrieval ① BM25로 top-M 문서 검색 ② 이를 포함한 QA 프롬프트로 LLM에 답변 생성 ③ Query와 Answer를 Concat → 재검색 ⇒ Retrieval 품질 향상 |
| ⚙️ 방법 구성요소 | - Retriever: BM25 (no training) - Answer Generator: GPT-3.5-turbo 또는 GPT-4 - Prompt 구성: “질문과 문서들(대부분 틀림)을 보고 정답 문서를 생성하라” - Augmented Query: q + a₁ + q + a₂ + ... 형식의 다중 답변 포함 |
| 📊 실험 설정 | - Zero-shot, few-shot, fully-supervised 방식과 비교 - MS-MARCO 기반 DL19, DL20 - BEIR 6개 세부 데이터셋 (SciFact, ArguAna 등) - 평가 지표: nDCG@10, MAP, Recall@1k |
| 🧪 실험 결과 요약 | DL19 (nDCG@10) BM25: 50.6 → HyDE: 61.3 → LameR: 69.1 DL20 (nDCG@10) BM25: 48.0 → HyDE: 57.9 → LameR: 64.8 BEIR: 4/6 태스크에서 LameR이 최고 성능 GPT-4 사용 시 DL20에서 65.9 기록 (DPR보다 높음) |
| 🔍 성능 향상 근거 | - BM25 기반이므로 LLM 출력이 텍스트로 직접 검색에 반영 가능 - LLM이 candidate 문서를 기반으로 domain/format/unit에 맞춘 정답 생성 → 정확도 및 domain alignment 증가 - 실험적으로 HyDE 대비 +7~8% nDCG@10 향상 |
| 📈 실효성 평가 | ✅ 성능 효과 있음: zero-shot setting에서 few-shot보다 높은 성능 ✅ 추론 기반으로 성능 상승의 원인이 명확: in-domain 문서 기반 prompt ✅ 모델 학습 필요 없음: 구축이 매우 쉬움 ✅ 검색 속도 빠름 (BM25) |
| ✨ 기여 | - 학습 없는 LLM+BM25 조합만으로 SoTA 성능 - LLM의 언어적 능력과 전통 검색 간의 조화 실현 - 다양한 실험과 ablation을 통해 방법론의 설계 근거를 정량적 검증 |
| ⚠️ 한계 | - Prompt 민감성: LLM의 질은 프롬프트 품질에 따라 달라짐 - LLM 호출 비용: inference-only지만, 응답 생성 비용은 여전히 존재 - ArguAna 등 긴 문서에 약함 (128 토큰 truncate) |
| 📌 후속 연구 가능성 | - 작은 LLM으로 대체해 효율성 ↑ - 2nd-stage reranking 모델 결합 - Retrieval diversity 확보 방안 필요 (2nd round 성능 감소 현상 발견) |
https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.16672
Jina-ColBERT-v2: A General-Purpose Multilingual Late Interaction Retriever
Multi-vector dense models, such as ColBERT, have proven highly effective in information retrieval. ColBERT's late interaction scoring approximates the joint query-document attention seen in cross-encoders while maintaining inference efficiency closer to tr
arxiv.org
| 🔍 문제 상황 | - 기존 ColBERT는 영어 기반으로만 학습되어 다국어 환경에 일반화 부족 - 기존 ColBERT는 하나의 고정 차원 임베딩만 사용 → 효율성과 유연성 부족 - 다국어 멀티 벡터 모델(BGE-M3 등)은 표현력이 높으나 메모리 비효율성으로 실용성 낮음 |
| 🧪 방법론 개요 | ColBERT 기반의 다국어 확장 모델로 다음을 도입: ① XLM-R 기반의 다국어 백본 ② 다중 차원 임베딩 학습 (Matryoshka Loss) ③ 2단계 학습(Pair + Triplet) ④ FlashAttention + RoPE로 효율 향상 ⑤ Hard Negative + CE Distillation |
| 🏗 모델 구조 | - Backbone: XLM-RoBERTa + RoPE + FlashAttention - Token Embedding Projection: 6개 차원(d ∈ {64,96,128,256,512,768})에 대해 joint training - MRL (Matryoshka Representation Loss): 다양한 차원 동시 학습으로 추론 시 선택적 사용 가능 |
| 📚 학습 데이터 | 🔹 Pair Training (사전학습) ‣ 총 4.5억 문장쌍, 영어 50%, 29개 언어 포함 ‣ Sentence pairs / QA / Query-Doc 쌍 🔹 Triplet Training (파인튜닝) ‣ MSMARCO, DuReader, MIRACL, NQ 등 + 기계번역 + 생성 데이터 포함 ‣ 총 14개 언어, 하드 네거티브 포함 ‣ Teacher: jina-reranker-v2-base-multilingual |
| 🧠 학습법 | 2단계 학습 파이프라인 ① Pair Training (contrastive loss): ‣ InfoNCE 기반 단일 벡터 유사도 학습 ‣ Temperature τ=0.02, LR=5e-5, BS=16384, 10만 step ② Triplet Training (KL loss distillation): ‣ CE 기반 soft label distillation ‣ LR=1e-5 (cosine decay), BS=32, BF16 precision, gradient clipping 적용 |
| 📊 실험 | 총 4개 벤치마크 실험: ① BEIR (nDCG@10) → ColBERTv2보다 평균 개선 ② LoTTE (Success@5) → ColBERTv2보다 +4.4 향상 ③ MIRACL (nDCG@10) → 대부분 언어에서 mDPR-FT 수준 혹은 상회 ④ mMARCO (mRR@10) → ColBERT-XM 대비 전반적 향상 |
| 🧪 Ablation 실험 | - MRL vs MRL-E: MRL-E 성능 저하 → MRL 사용 - [MASK] token attention 허용: 성능 개선 (특히 비영어) - Natural Language Instructions 사용: 성능 감소 (Late interaction과 부적합) - Score Normalization (KL): 효과 미미 |
| 🏆 기여 | ✅ ColBERT 구조에 기반한 최초의 다국어 범용 모델 ✅ MRL + multi-head projection으로 embedding dimension 선택 가능 ✅ Weak-to-Strong 학습 파이프라인 설계 ✅ 다양한 다국어/도메인에 대해 우수한 성능과 실용성 확보 |
| ⚠️ 한계 | - ArguAna (긴 쿼리, 반대 주장 검색 등)에서는 성능 저하 - mDPR-FT 같은 언어 특화 모델에는 근소 열세 - Triplet 학습시 7개 네거티브만 사용 (ColBERTv2의 32/64보다 적음) |
https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.01753
Boolean-aware Attention for Dense Retrieval
We present Boolean-aware attention, a novel attention mechanism that dynamically adjusts token focus based on Boolean operators (e.g., and, or, not). Our model employs specialized Boolean experts, each tailored to amplify or suppress attention for operator
arxiv.org

규칙 기반이라.... 음... 딱히
| 문제 상황 | 기존 Dense Retriever (ex. BERT)들은 Boolean 논리(AND, OR, NOT)를 explicitly 처리하지 못함 - 특히 NOT (부정)은 의미를 왜곡하거나 오히려 강조하는 문제 발생 - Boolean 질의에서는 정확한 논리적 관계가 중요함 (e.g. “A and B but not C”) |
| 제안 방법 | Boolean-aware Attention (BoolAttn) 기존 self-attention에 Boolean 논리 구조를 반영한 bias를 추가하여 query 구조를 해석 가능하게 함 |
| 모델 구성 | BERT에 다음 모듈들을 삽입한 Bool-BERT: ① Cue Predictor: “and”, “not” 등 Boolean cue 위치 식별 ② Scope Predictor: cue로부터 영향을 받는 token 범위 (scope) 예측 (Conv1D + FiLM) ③ Bias Predictor: cue와 token 간의 거리 기반으로 attention bias 계산 (Gaussian kernel 사용) ④ Gating Mechanism: 현재 query에 등장한 연산자에 따라 expert 모듈 활성화 → 최종적으로 S_attn = Sand + Sor - Snot 형태로 attention bias 구성 |
| 학습 데이터 | 🔹 Pretraining: GPT 기반 Boolean query 데이터 (Mai et al., 2024) - Boolean cue 탐지 (cue classification) - 연산자 존재 여부 예측 (multi-label expert classification) 🔹 Downstream Fine-tuning: - QUEST: Boolean 질의를 포함한 entity-seeking retrieval dataset - BoolQuestions: MS MARCO 기반 Boolean QA dataset |
| 학습 방식 | Dual-encoder 방식 (BERT 기반 Dense Retriever) - Query: Bool-BERT, Document: BERT - 매 step마다 positive document를 random shuffle (multi-answer 대응) - Hard negative 대신 BM25-negative나 random-negative 사용 - Pretrain 시 CuePred와 Gate만 업데이트, ScopePred & BiasPred는 triplet loss로 가볍게 초기화 |
| 실험 설정 | - Batch size: 32 - Optimizer: AdamW - lr=5e-5, weight decay=0.01 - Epoch: 40 - Max query length: 64 - Max doc length: 256 |
| 실험 결과 | 🔹 QUEST (Recall@K) - Bool-BERT-base: 0.483 (vs BERT-base: 0.443) - Bool-BERT-large: 0.495 (vs BERT-large: 0.467) 🔹 BoolQuestions (MRR@10) - NOT: 0.165 (vs BERT 0.128) - AND: 0.480 → 0.532, OR: 0.586 → 0.610 |
| 기여 | ✅ Boolean 논리를 반영하는 attention bias 설계 ✅ Transformer에 모듈형으로 삽입 가능 (plug-and-play) ✅ NOT 연산자의 부정 효과를 downweight하여 retrieval 오류 감소 ✅ BERT 기반 모델의 Boolean 질의 해석력 개선 |
| 한계 | ❌ 약 10%의 파라미터 증가 → 연산량, latency 증가 ❌ CuePredictor 오류 시 Scope/Bias 오류로 전파 (error propagation) ❌ 암묵적 Boolean 표현 ("favoring A over B")은 탐지 어려움 ❌ Scope에 대한 ground-truth 없음 → 간접 학습만 가능 ❌ Boolean dataset 규모가 작아 generalization 어려움 |
| 활용 가능성 | 🔸 Retrieval 기반 QA에서 부정어 처리, 복합 조건 검색에 강함 🔸 Open-domain QA, Medical IR, Legal Search 등 정확한 조건 필터링이 필요한 상황에 활용 가능 |
https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.01651
Efficient Length-Generalizable Attention via Causal Retrieval for Long-Context Language Modeling
Despite the success of Transformers, handling long contexts remains challenging due to the limited length generalization and quadratic complexity of self-attention. Thus Transformers often require post-training with a larger attention window, significantly
arxiv.org

| 🔍 문제 상황 | - 기존 Transformer는 길이 일반화(length generalization)에 약하고 - Self-Attention은 O(n²) 복잡도로 긴 context 처리에 비효율적. - Retrieval 기반 모델(RLM)도 retriever가 token loss로부터 학습 불가하여 end-to-end 학습이 불가능. |
| 🧠 제안 방법 | 1. Grouped Cross-Attention (GCA) - Chunk별 relevance score를 계산하여 Cross-Attn 수행 후 weighted sum. - 이 relevance score는 token prediction에 직접 영향을 주므로 gradient 전달 가능 → retriever 학습 가능 2. Differentiable Retrieval-based Transformer (DRT) - Lower Layer: sliding window attention - Upper Layer: G개 그룹으로 나눠 각 그룹마다 GCA 수행 |
| 🏗 모델 구조 | - 12-layer decoder-only Transformer (6 lower + 6 upper) - Hidden dim 768, FFN dim 2048, 12 heads - Sliding window: 512 tokens - Chunk size: 64 tokens - Top-k retrieved chunks: 8개 - 각 chunk에 Landmark Token 삽입 (내용 요약 및 relevance 계산 용) |
| 🧪 학습법 | - Optimizer: AdamW (β₁=0.9, β₂=0.95, weight decay=0.001) - Learning rate: 2e-3 → cosine decay to 4e-4 - Tokenizer: GPT-2 - Mixed precision (bfloat16) - 8 A100 GPU에서 32.2B tokens 학습 - Training step: 60K, context length: 16K tokens |
| 📚 학습 데이터 | - PG19: 장문 소설 기반 long-range LM 평가용 - ArXiv-math: 수학 논문 기반, 정의/정리 등 먼 거리 문맥 추론 필요 - Summarization: XSum, CNN/DM - NIAH benchmark: passkey를 먼 context에서 추론해야 하는 synthetic benchmark |
| 🧪 실험 | Long-range LM (PG19, ArXiv-math) - context 16K로 학습한 DRT가 16M까지 generalization 가능 - Landmark Attention보다 길이 일반화 성능 우수 Downstream Tasks - XSum, CNN/DM summarization → ROUGE 점수 우수 NIAH Test - DRT: 16M 토큰까지도 100% passkey retrieval 정확도 유지 - Landmark Attn은 32K 이상에서 성능 급감 |
| 🏁 결과 요약 | - DRTretrieval×2 > DRTretrieval×1 > 모든 baseline - GCA는 inference memory 효율성, throughput에서도 LA 대비 압도적 - Multiple retrieval (G>1)은 성능 향상에 유의미함 |
| 🧩 기여 | ✅ 최초로 16M context 길이에서 100% 정확도로 passkey retrieval 성공 ✅ retriever도 end-to-end 학습 가능한 attention 방식 (GCA) 최초 제안 ✅ sliding window + GCA 조합으로 O(L) 복잡도 달성 ✅ 실험에서 길이 확장성 + 성능 + 효율성 모두 우수함 입증 |
| ⚠️ 한계 | - Retrieval은 context 내부에 한정됨 (외부 메모리 미포함) - GCA는 chunk 기반이기 때문에 token-level granularity는 낮음 - landmark token 설계나 chunk size 선택에 따라 성능 민감 가능성 있음 |
| 🔭 향후 연구 | - Context 외부 대규모 메모리에서 self-supervised causal retrieval 확장 - multi-granular structured representation 기반 retrieval과의 결합 예정 |
https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.17010
Generative Retrieval with Large Language Models
When completing knowledge-intensive tasks, humans sometimes need not just an answer but also a corresponding reference passage for auxiliary reading. Previous methods required obtaining pre-segmented article chunks through additional retrieval models. This
arxiv.org

| 🔍 문제 상황 | - 기존 dense/sparse/generative retrieval은 대부분 사전 분할된 passage만 다룸 → 자유로운 위치 선택 불가능 - dense retriever (e.g., DPR)는 shallow한 interaction만 가능 - LLM은 지식 기억을 가지고 있지만, 자유롭게 "정답 문장"을 꺼내는 방식은 연구 부족 |
| 🧠 제안 방법 (LLM2GR) | LLM이 human-like recall을 하도록 2단계 구조의 generative retrieval 방법 제안: ① 문서 제목 recall: Trie를 사용해 존재하는 Wikipedia 제목만 생성 ② 본문 passage recall: FM-Index 기반으로 문서 내 arbitrary 위치에서 short prefix 생성 → 위치 추출 → passage 복원 |
| ⚙️ 모델 구조 | - Base LLM: LLaMA, LLaMA2 (7B, 13B) - 1단계: Trie 기반 constrained decoding - 2단계: FM-Index + KMP로 위치 탐색 - Passage 점수 = 제목 점수와 weighted sum |
| 🏋️ 학습 및 추론 방법 | - Zero-shot prompting만 사용 (fine-tuning 없음) - Beam Search 기반 생성: 1단계 beam=15, 2단계 beam=10 - Prefix 길이: 16 tokens, 추출 passage 길이: 150 tokens - Score weight: α=0.9 (제목 recall 가중치 높임) |
| 📚 사용 데이터 | - KILT benchmark의 6개 task ∙ NQ, TriviaQA, HotpotQA, ELI5, FEVER, WoW - validation set 기준 평가 (test set 비공개) |
| 📈 실험 결과 | ✅ Page-Level (R-Precision): ∙ NQ: 57.77 / HotpotQA: 48.70 / FEVER: 83.69 (LLaMA2-13B) ✅ Passage-Level (Answer in Context): ∙ TriviaQA: 68.20 / FEVER: 58.42 / WoW: 63.43 ✅ Downstream Task 성능: ∙ TriviaQA EM: 31.69 (DPR보다 높음) ∙ WoW F1: 14.77 (최고 성능) |
| 📊 Ablation Study | - ❌ w/o Trie (1단계 제거): coarse & fine 성능 모두 급락 → 제목 recall 중요성 입증 - ❌ w/o SPRL: 전체 passage 생성 → 느리고 noise 증가 - ❌ w/o weighted score: 최종 선택 precision 낮아짐 |
| 💡 주요 기여 | - LLM을 이용한 retrieval-free reference recall 최초 제안 - Trie + FM-index 기반 제약 생성으로 hallucination 방지 - Short Prefix 기반 SPRL로 inference 시간 4배 단축 - Zero-shot 기반이면서도 dense retriever보다 성능 우수 or 유사 |
| ⚠️ 한계 | - DPR 등 fully-supervised retriever보단 성능이 낮은 경우도 있음 - 제목 없는 문서 또는 pretrain에서 드물게 등장한 문서 recall 어려움 - 새로운 문서를 다루려면 추가 학습 또는 index 업데이트 필요 |
| 🔮 향후 방향 | - Instruction tuning 통한 recall 능력 강화 - Multi-hop reasoning 통합 - Lightweight하게 LLM에 신규 지식 삽입하는 방식 연구 |
'인공지능 > 논문 리뷰 or 진행' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Language Model의 Representation 능력 논문 1 (5) | 2025.08.05 |
|---|---|
| SHEARED LLAMA: ACCELERATING LANGUAGEMODEL PRE-TRAINING VIA STRUCTURED PRUNING (9) | 2025.08.04 |
| Embedding(Retriever) 모델 논문 1 (0) | 2025.07.27 |
| soft prompting 관련 논문 정리 1 (7) | 2025.07.22 |
| Qwen3 Embedding: Advancing Text Embedding and Reranking Through Foundation Models (1) | 2025.07.21 |